Imagine clean tap water running just once a week, or half the population struggling to rustle up a single meal every day. This, according to Eddie Cross, an MP for Bulawayo South and founding member of the opposition Movement for Democratic Change (MDC) party, is the reality of a “period of harsh austerity” in Zimbabwe that “has [drastically] reduced living standards”.
These tough conditions show little sign of letting up, with the country sinking deeper into an economic crisis that has drawn comparisons to 2008, when GDP growth in Zimbabwe fell to -17.7 percent (see Fig 1) and the currency was devalued to such an extent that a wheelbarrow full of notes wouldn’t even buy a loaf of bread.
In the aftermath of the 2008 hyperinflationary crisis, the country’s leaders were able to agree on a power-sharing arrangement that allowed Zimbabwe to emerge with some semblance of hope. This time round, with the nation’s ruling party refusing to relinquish control or acknowledge the depths of the crisis, no solutions – international or domestic – are forthcoming. Rather, the country seems doomed to sink deeper into a financial depression that will have devastating consequences for its citizens and could take decades to recover from.
Rocky Rhodes
In its short history as a unified country, Zimbabwe has seen its fair share of economic hardship. The area of land that makes up modern-day Zimbabwe had been home to various tribal communities for centuries before it was demarcated in its current form in the 1890s by imperialist Cecil Rhodes and the British South Africa Company. The new state, which was named Southern Rhodesia in honour of its coloniser, remained under the control of the UK until 1965, when it declared itself independent. The following 15 years would be defined by a brutal civil war, which pitted the white colonialist minority government against black guerrilla forces led by, among others, future Zimbabwean Prime Minister Robert Mugabe.
Zimbabwe seems doomed to sink deeper into a financial depression that will have devastating consequences for its citizens
Peace was achieved in the early 1980s, facilitating Zimbabwe’s emergence as an economic star. The country’s GDP grew by an average 5.2 percent during that decade, thanks to an extensive programme of public spending – notably on education and healthcare facilities. In 1992, a study by the World Bank found that more than 500 health centres had been built across the country in the preceding 12 years, while enrolment in secondary schools had increased by 902 percent between 1980 and 1990. For all intents and purposes, the country was well on its way to becoming mythologised as a great African success story.
Mugabe’s administration, however, made a series of poor decisions that impeded the country’s economic ascendance. The first was the manner in which the early 1980s investment drive was carried out. As a fledgling independent nation, Zimbabwe did not have the necessary productivity to support such high spending, so while the new societal infrastructure improved the quality of life for Zimbabwe’s citizens, it also meant the country racked up a significant budget deficit, leaving it extremely short on emergency funds.
The government’s second misstep came in 1998, when it chose to weigh in on the conflict in the neighbouring Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Not only did the cost of this intervention drain what little remained of Zimbabwe’s bank reserves, it also alienated the country from the international community – in 1999, both the World Bank and the IMF suspended their aid provision due to an unwillingness to fund Zimbabwe’s military spending in the DRC. Three years later, the country was suspended from the Commonwealth and subjected to sanctions by both the US and EU amid allegations of political corruption. This isolation decimated Zimbabwe’s agricultural sector, which accounted for around 12.6 percent of GDP at the time.
“Zimbabwe was an agrarian industrial country, with emphasis on the word ‘industrial’,” Stephen Chan, a professor of international relations at SOAS University of London, told World Finance. “It was regarded as extremely hi-tech, growing food for modern international markets.” The application of sanctions, however, severely dampened exports. The industry was further crippled by a drought in 2003, which destroyed the meagre subsistence agriculture that remained and left 70 percent of Zimbabwe’s citizens living below the bread line.

Sick notes
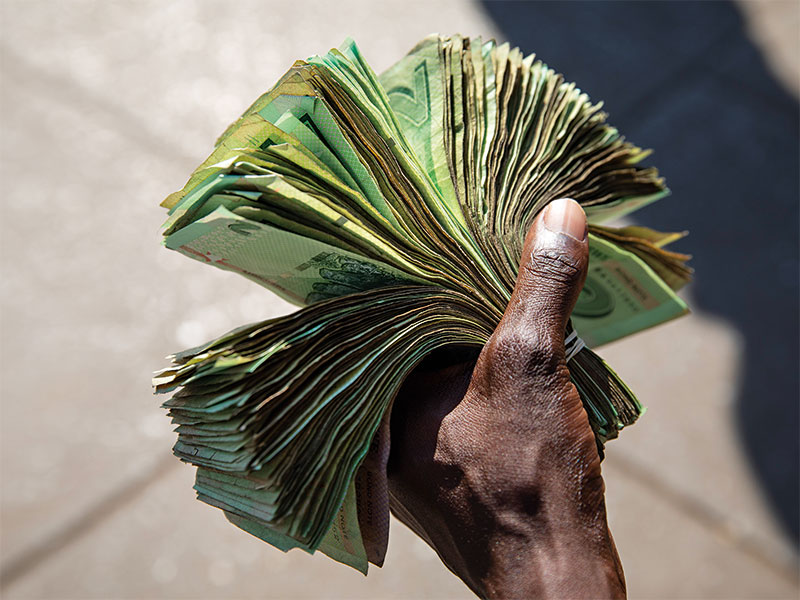
Over the following five years, the country descended deeper into economic crisis. Inflation reached 1,000 percent in 2006 – leading the World Bank to declare Zimbabwe the fastest-shrinking economy outside of a war zone – and the government’s attempts to stop prices from skyrocketing were ineffectual, to say the least. While Gideon Gono, the former governor of the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, claimed hyperinflation peaked at 2.2 million percent in July 2008, Bloomberg estimates it was closer to 500 billion percent – a figure that Chan described as “metaphysical”. He added: “You couldn’t offer beggars anything in the street, because they’d just throw it away. It was meaningless. You’d have entire alleyways just full of worthless notes.”
Chan’s vivid image symbolises a wider truth: currency has always been at the heart of Zimbabwe’s economic troubles. In the 1980s and 1990s, as the country remained in relative infancy, one of the most vital tasks for Mugabe’s administration was to ensure the Zimbabwean dollar retained its value in order to support macroeconomic stability. It failed dismally for two reasons: first, it showed an inability to create and maintain national industries that would offer underlying productive value, and second, it proved itself too willing to devalue the currency, which, in turn, caused a greater international PR problem.
The destructive impact of the government’s failure was borne out most clearly in the hyperinflation crisis, but the repercussions continue to this day. In 2009, then finance minister Tendai Biti, who was part of an emergency government of national unity, implemented a recovery plan centred on the adoption of the US dollar as legal tender. While this succeeded in curbing hyperinflation at the time, it has subsequently caused significant issues when it comes to obtaining foreign currency – particularly given the rest of the world’s reluctance to lend to Zimbabwe, which stems from the country’s failure to prove that it has learned its fiscal lesson. “What has come home to roost very recently is that [Zimbabwe] really has no way of sourcing any more dollars,” Chan told World Finance. “No one will lend to [it] anymore, because there never really was a viable repayment plan.”

The government has not been entirely oblivious to these shortages and has, over the past few years, attempted to introduce various currency policies, each with little success. In 2016, bond notes and coins that would purportedly mirror the value of the US dollar were introduced, but they rapidly lost value when citizens realised they had no inherent worth and were not widely accepted as payment. In June 2019, the government – now led by President Emmerson Mnangagwa following the ousting of Mugabe in a military coup in 2017 – went a step further and attempted to introduce an entirely new currency. The RTGS dollar – the first iteration of Zimbabwe’s sovereign currency since 2008 – prevents citizens from using foreign currencies such as the US dollar and pound sterling as legal tender.
In August 2019, Zimbabwean Foreign Minister Sibusiso Moyo claimed that introducing the new currency had stabilised the economy, but with the government refusing to publish inflation data until February 2020, it’s difficult to know whether there’s much truth in his statement. Chan is unconvinced: “There was no real choice because of the lack of US dollars, but there’s no productive value [in the new currency] to pay for imports, so wholesalers are just going to charge more and more money for things.” In other words, the government’s reluctance to reveal inflation information smacks of a cover-up – it does not want to reveal to the world exactly how much of a failure its initiative was with regards to curbing inflation.
Trouble ahead
Anecdotal evidence emerging from Zimbabwe does little to suggest the government has averted an economic crisis. As of June, fuel prices had been hiked to such an extent that the average daily commute costs as much as $20, while 18-hour blackouts have become commonplace in Zimbabwe’s capital, Harare. According to the World Food Programme, an estimated two million people are facing drought-induced starvation, while the same number have no access to clean water.
The current scarcities pose an immediate threat to life for some of Zimbabwe’s citizens, but there are also deeper and more wide-reaching disasters on the horizon, particularly with regards to shortages in HIV and AIDS medication. According to the UN, the country has one of the highest prevalences of HIV in sub-Saharan Africa, with an estimated 12.7 percent of the population living with the disease in 2018. This figure has fallen dramatically from its peak in the early 2000s – thanks, in part, to increased awareness of transition methods and behavioural changes such as the use of condoms. Access to antiretroviral treatment (ART) has also improved as a result of a government programme that started to be rolled out in 2003.
According to the UN, 84 percent of those living with HIV in Zimbabwe were able to access ART in 2018. Within this group, 70 percent were provided with medication by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, a multinational organisation that provides grants to nations where HIV is prevalent. In order to unlock these grants, however, governments must contribute a certain percentage of the cost; in Zimbabwe’s case, its leaders must pay $24.2m between 2018 and 2021 to gain access to the full $483m grant.
As a result of the financial troubles currently afflicting the country, the Zimbabwean Government was unable to contribute the $6m sum required in July to unlock the Global Fund’s latest instalment. Consequently, access to ART for HIV patients has been severely restricted, with some being issued a two weeks’ supply at a time rather than the requisite three months, and others being given expired drugs.
“You’ve got the makings of a second stage of the pandemic [of the 1980s],” Chan said. If HIV sufferers cannot gain access to the life-saving medication needed to control their symptoms, cases of AIDS are likely to surge. Infection rates may also rise, as sufferers will not be visiting clinics to collect medication and, as a result, will not be offered condoms at the same time.

Mine for the taking
Of course, not all of Zimbabwe’s citizens are suffering. “There’s an oligarchic class made up of elite governmental and military figures – or those related to such people – who have insulated themselves by some recourse to corrupt means,” Chan explained. Members of this class, which established itself during Mugabe’s reign and has gone unchallenged by Mnangagwa, reportedly enriched themselves through a combination of bribery, overvalued government contracts and the illegal seizure and sale of illegitimate property.
“Transparency International estimates that $100bn has disappeared from the Zimbabwean economy [as a result of corruption],” Cross told World Finance. “The military has been a major beneficiary and has fought to protect its privileged position [under Mnangagwa].” What’s more, this corruption is not the sort that offers a silver lining in the form of job creation or productive value. “Corrupt monies circulated within can be beneficial, even if not always traceable,” Chan said. “But when it’s taken out of the system – or spent on non-productive luxuries, as is largely the case in Zimbabwe – no good is done.”
The diamond market has proven a particularly popular breeding ground for corruption, with a 2008 cable (leaked in 2010) from the US Embassy in Zimbabwe calling the sector “one of the dirtiest” in a “country filled with corrupt schemes”. In 2006, Zimbabwe became a diamond hotbed overnight following the excavation of the Marange diamond fields, which were regarded at the time as the richest natural source of the gems to be discovered for more than a century.
It was hoped initially that the government would utilise the funds derived from mining to reduce the country’s budget deficit; in practice, though, profits have been concentrated in the hands of a select few political and military officials. According to the 2008 cable, these include Gono and former vice president Joice Mujuru, both of whom were accused of skimming hundreds of thousands of dollars a month in illegitimate profits from gem sales. Both Gono and Mujuru denied these allegations.
The Marange diamond fields were also reported to be the site of a torture camp run by the Zimbabwe National Army, the existence of which was revealed in 2011 by the BBC’s Panorama series. Victims told the broadcaster they had been subjected to beatings, sexual assault and dog maulings at the hands of the soldiers there, none of whom are known to have faced repercussions for their actions.
With the government paralysed by a crisis of its own creation, Zimbabwe’s citizens have been left to weather the storm alone
Military impunity remains a significant issue in Zimbabwe today. Not only does this reinforce the existence of corruption, it also creates a culture of fear and violence, robbing citizens of their right to peaceful protest. In January 2019, when trade unions led a work stoppage following a 150 percent hike in fuel prices, security forces shot dead 17 people and raped at least 17 women, according to Human Rights Watch.
No way out
Given the endemic nature of corruption, the dire economic situation and looming public health crisis, the outlook for Zimbabwe is bleak. The most pressing challenge remains the restoration of some kind of economic stability, but with other countries unwilling to offer budgetary support loans and national industry at a standstill, the government will be hard-pressed to drum up any sort of funding soon. Even if it did stumble upon some miraculous money tree, the notes growing on its branches would either be entirely worthless or not accepted as legal tender in accordance with current monetary policy. What’s more, given the level of corruption at the uppermost levels of government, it’s highly unlikely that any new funds would be directed to the sectors suffering critical shortages. Instead, they would find themselves lining the pockets of the well connected.
With the government paralysed by a crisis of its own creation, Zimbabwe’s citizens have been left to weather the storm alone – a nigh impossible task given the absolute lack of basic societal infrastructure. Even the informal economy, which has historically proven extremely resilient in Zimbabwe, is floundering. Last year, in a bid to maintain some sort of viable currency regime, a number of small operators began establishing a grassroots virtual economy, using mobile cash to pay for goods and services. However, this was quickly quashed by the country’s conservative-leaning finance minister, Mthuli Ncube, who introduced a two percent tax on transactions that priced out low-earning citizens.
In a functioning democratic society, the clear response to such an abject failure in economic policy would be to vote out the politicians responsible. In Zimbabwe, though, this is not an option given the monopoly held by Mnangagwa’s party, the Zimbabwe African National Union Patriotic Front (ZANU-PF). Even if there were to be an election, the likelihood of the results being manipulated is extremely high. What’s more, ZANU-PF’s main opposition, the MDC, is by no means squeaky clean, having experienced its own corruption scandals in recent years. “If you’re looking at democratic solutions for the future, then Zimbabwe is currently between a rock and a hard place,” Chan told World Finance.
The one glimmer of light at the end of the tunnel is Zimbabwe’s negotiations with the IMF regarding a bailout programme, which remain at an early stage. However, the IMF is highly unlikely to green-light any loans until Zimbabwe pays off its debts to other lenders, such as the World Bank. Even if loan agreements can be reached, the country will pay a high price for financial assistance. “Terrible austerities have to come and the poorest people will be hit the hardest,” Chan said. This would likely lead to further civil unrest, again culminating in military violence.
As it currently stands, Zimbabwe is a ticking time bomb. With domestic options exhausted, international intervention is crucial to supporting and sustaining the lives of its citizens. If the country is allowed to collapse entirely, the implications will stretch well beyond Zimbabwean borders, leaving the rest of the world to pick up the humanitarian and economic pieces for decades to come.